Neurological Conditions

1. What is Peripheral Neuropathy?
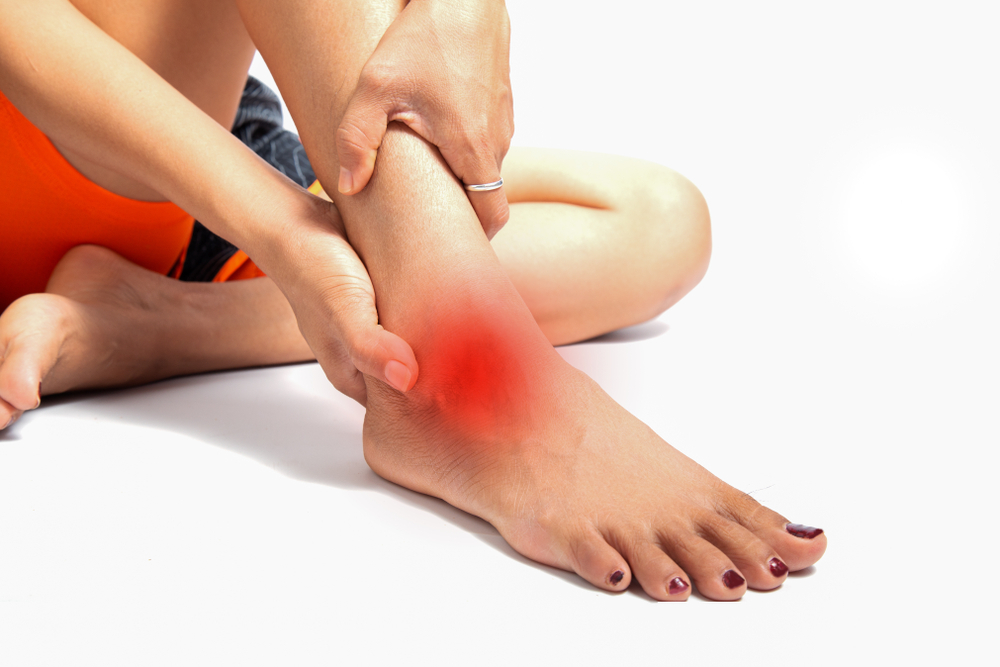
Peripheral Neuropathy is a disorder that causes a malfunction in your Peripheral Nervous System, causing it to send mixed signals such as pain when no pain is inflicted or won’t signal the pain when it is. The Peripheral Nervous System connects your body’s nerves to the brain and the spinal cord to the rest of your body.
The peripheral nervous system helps by sending signals for your body to react in certain situations. Peripheral nerves are like an intricate network of roads that connects your brain and spinal cord to your muscles, skin, limbs, internal organs, and even mouth. These peripheral nerves come out of your spinal cord arranged in lines known as Dermatomes. If any damage occurs to the dermatomes, it could affect more dermatomes and could be tracked to the specific area of the damage. This malfunction occurs due to some of the nerves getting damaged or destroyed. Various factors could cause such results, such as an injury or a systematic illness, or even an infection, disrupting communication between your brain and body, causing impaired movements, no sensation in your limbs, and mixed reactions to various situations.
2. What are the symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy?
Peripheral Neuropathy is a disorder that causes a malfunction in your Peripheral Nervous System. This disrupts communication between your brain and body, causing impaired movements, no sensation in your limbs, and mixed reactions to various situations.
There are three different types of Peripheral nerves,
- Sensory nerves, which connect the nervous system to your skin.
- Motor nerves, which connect to your muscles.
- Autonomic nerves connect to your internal organs.
Peripheral Neuropathy could affect any one of these types or even all of them, which could lead to causing various symptoms such as:
- Tingling sensation in your hands and feet.
- Feeling of having very tight gloves on your hands and socks on your feet.
- Stabbing pains, needle pricks.
- Feeling of numbness in your palms and feet.
- A heavy and weak feeling in your arms and legs also causing your limbs to lock in a place.
- Dropping things from your hands.
- Causing a buzzing or shocking sensation.
- Low blood pressure.
- Sexual dysfunction, commonly in men.
- Low bowel movement causing constipation.
- Digestive impediment.
- Diarrhoea
These symptoms could also result from other conditions; ensure you contact your doctor and inform them about the symptoms.
- What is Peripheral Neuropathy?
Peripheral Neuropathy is a disorder that causes a malfunction in your Peripheral Nervous System, causing it to send mixed signals such as pain when no pain is inflicted or won’t signal the pain when it is. The Peripheral Nervous System connects your body’s nerves to the brain and the spinal cord to the rest of your body.
The peripheral nervous system helps by sending signals for your body to react in certain situations. Peripheral nerves are like an intricate network of roads that connects your brain and spinal cord to your muscles, skin, limbs, internal organs, and even mouth. These peripheral nerves come out of your spinal cord arranged in lines known as Dermatomes. If any damage occurs to the dermatomes, it could affect more dermatomes and could be tracked to the specific area of the damage. This malfunction occurs due to some of the nerves getting damaged or destroyed. Various factors could cause such results, such as an injury or a systematic illness, or even an infection, disrupting communication between your brain and body, causing impaired movements, no sensation in your limbs, and mixed reactions to various situations.
2. What are the symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy?
Peripheral Neuropathy is a disorder that causes a malfunction in your Peripheral Nervous System. This disrupts communication between your brain and body, causing impaired movements, no sensation in your limbs, and mixed reactions to various situations.
There are three different types of Peripheral nerves,
- Sensory nerves, which connect the nervous system to your skin.
- Motor nerves, which connect to your muscles.
- Autonomic nerves connect to your internal organs.
Peripheral Neuropathy could affect any one of these types or even all of them, which could lead to causing various symptoms such as:
- Tingling sensation in your hands and feet.
- Feeling of having very tight gloves on your hands and socks on your feet.
- Stabbing pains, needle pricks.
- Feeling of numbness in your palms and feet.
- A heavy and weak feeling in your arms and legs also causing your limbs to lock in a place.
- Dropping things from your hands.
- Causing a buzzing or shocking sensation.
- Low blood pressure.
- Sexual dysfunction, commonly in men.
- Low bowel movement causing constipation.
- Digestive impediment.
- Diarrhoea
These symptoms could also result from other conditions; ensure you contact your doctor and inform them about the symptoms.
3. What are the causes of Peripheral Neuropathy?
Various things can lead to causing Peripheral Neuropathy; mainly, all these causes are a part of three different types of origin of Peripheral Neuropathy.
- Acquired Neuropathy.
- These are caused due to various environmental factors such as toxins, infection, and illness as well. The different Acquired Neuropathy causes are,
- Alcoholism can have a highly toxic effect on your nerve tissues.
- Vitamin deficiency or insufficient nutrition supply.
- Diabetes.
- Particular kind of cancer and its chemotherapy treatment.
- Multiple rare inherited diseases.
- Conditions that cause your nerves to get damaged by your immune system due to an overaggressive response.
- Kidney, which causes a high amount of toxins in the body and damages nerve tissues, thyroid disease
- Various infections such as Lyme disease, Shingles, AIDS. Viruses such as herpes simplex or varicella-zoster virus cause chickenpox and damages sensory nerves, causing intense events of pain
- Hereditary Neuropathies.
These are not the most common causes of any Peripheral neuropathy; the diseases are generally passed on from one generation to other. The most common of these is Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, which causes weakness in your legs and arms; the symptoms regarding this disease usually don’t appear until mid-childhood or in your 30s.
Idiopathic Neuropathies.
These are usually the often cases in the most cause of Peripheral Neuropathy. In this, the leading cause or the origin of the disease remains unknown or not classified.
4. What are the treatment options available for Peripheral Neuropathy?
Even though there is no cure for this disease, it can be controlled by treatment. The treatment options are based on the underlying disorder which caused it and not on peripheral Neuropathy itself. If a patient has diabetes and it is the cause, then getting it in control by making its blood glucose normal will be the treatment. There are various treatments available that could bring back some activities and cause relief.
Pain Medications:
These can be very helpful to control the pain and the burning sensation caused due to peripheral Neuropathy’s symptoms. Pain medication such as acetaminophen and anti-inflammatory drugs like aspirins or ibuprofen help in these cases. Even though these are very helpful, they come with some side effects as they affect your liver and digestion functions.
Prescription Medication:
Your doctor will prescribe you specific medication based on your symptoms and pain medication suitable for your body to control the pain. The prescribed medications may include antiepileptic medicines and some antidepressants. The common medications could be Tramadol, Cymbalta, or corticosteroid injections. The medication may also be based on your sexual function.
Medical Treatments:
Your doctor will perform several treatments to control or lessen your symptoms. Blood transfusion can remove the potential vexatious antibodies from your bloodstream. There are various other treatments such as,
Transcutaneous electronic nerve stimulation places electrodes on your skin and sends small amounts of electricity into the skin; this treatment disrupts nerves from broadcasting pain signals.
Ergonomic casts can aid you in neuropathic effects in your limbs. The casts provide support to them and hold them a certain way for relieving the pain.
Self-care is essential for decreasing any of your pain and discomfort, exercise regularly and leisurely. If you have any smoking or drinking habit, it is crucial to cut back both as they cause nerve pain and nerve damage. Various people find peripheral Neuropathy through acupuncture, deep massages, meditation, and yoga. Taking precautions is also very important in treating yourself.
5. Is there any topical treatment available for Peripheral Neuropathy?
Peripheral Neuropathy cannot be cured, but there are surely some great treatments available to control any discomfort and pain caused by it. The treatment options are based on the underlying disorder which caused it and not on peripheral Neuropathy itself.
Before beginning any treatments and taking drugs, you should go through a proper diagnosis for your doctor to understand the cause and the appropriate treatment for you to go through. Generally, in most treatments, the initial medications given are pain killers, antidepressants, and antiseizure. This helps you be stable and relieve you from any pain or blazing sensation in your body.
Apart from all the medications and different medical treatments, your doctor may also suggest you some Topical Treatments. Capsaicin is the standard topical cream your doctor will recommend as it has a similar substance found in hot pepper which applied to the affected area helps repair peripheral Neuropathy. This cream does come with its side effects as it may burn or cause irritation due to its substances, and though it decreases, this may not be bearable for someone. There is another treatment from Lidocaine patches, which you can apply on your skin and get diverted from any pain as it mainly numbs you down or the portion you’ve used for not sensing any pain.
